Natural Selection
Natural selection is probably the most prominent mechanism of evolution. Proposed by Charles Darwin, the theory of natural selection gives an answer to how modern organisms evolved from past life. Individuals with the best traits for survival are able to survive and pass on their genes until the majority of the population possesses that advantageous gene, thus evolving the population. Additional information about natural selection can be found here.
Mutations
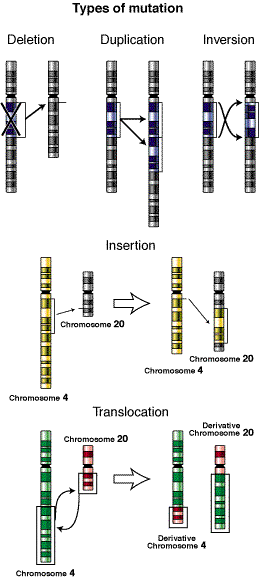
Mutations are chance alterations in nucleotide sequences (DNA) that can result in new phenotypes in resulting offspring. For example, two green beetles can reproduce and a mutation in nucleotide sequences could lead to the offspring being brown. Mutations lead to variation in the population which is the first step of evolution. There are various type of mutations, some being more drastic than others. It is also possible that a mutation can happen, and it have no real effect on the individual. Mutations tend to occur during DNA replication. The following are five different types of mutations:
Deletion
A segment of DNA is removed from the original DNA sequence. Can have no effect or drastic effects on an individual, it depends on what segment of DNA is effected.
Duplication
A segment of DNA is copied twice is repeating segments. Duplication may or may not have significant effects on the individual.
Inversion
When copied, the DNA segment is reversed in orientation. It would be like if you went to sleep with your head on one end and then when you wake up, your head is on the other end.
Insertion
A section of nucleotides is added in a place it should not. This could throw off the reading from and have significant effects on the individual.
Translocation
A portion of a nucleotide sequence is copied onto another nucleotide sequence.
 |
| DNA models depicting different types of mutations |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift refers to chance changes in the allele frequency that leads to the evolution of a species with a resulting allele frequency not necessarily indicative of the original population. There are two main types of genetic drift; founders effect and bottleneck effect. Founders effect when a smaller group of individuals become isolated from the original population and become the founders of a new one. The population then evolves based on selective pressures of their new environment and it could become completely different from the original population. Bottleneck effect refers to a chance event killing a group of individuals from the population. This could be as major as a storm wiping out much a population on an island, or as simple as a human stepping on a group of beetles. The resulting population is different from the original because of a chance encounter. The population will then recover and evolve based on the resulting allele frequencies after the bottleneck event, and the selective pressures in the given environment. The following video simulates genetic drift by depicting both founders and bottleneck effect.
Gene Flow
Gene flow refers to the changes in allele frequency in a population by individuals coming into, and leaving a population. This is similar to founders effect except the only difference is founders effect is a result of chance happenings. Gene flow is simply the influx and outflux of alleles in the population based on habitable area, availability of resources, and mates. Certain advantageous genes may enter a population as a result of gene flow and the population may evolve to acquire that advantageous trait.
Sexual Selection
Lastly, sexual selection refers to the selection of mates based on physical characteristics. It is usually female choice and they select mates based off what they find attractive. It could be anything from feather color, to length of tail, to size of muscles, all of these could be characteristics desirable to the opposite sex and cause them to reproduce. Sexual selection can result in the evolution of a species because if many females are drawn to the same aesthetic, they will continually reproduce with the males that present that trait. Over time, the population will evolve to mostly have that attractive trait.
No comments:
Post a Comment